It has been observed that home fires often occur during the holidays, while wildfires are more common in the summertime. However, the fact remains that fire can happen at any time. Being prepared and understanding the basics of fire safety, including common causes and first aid treatment, can save lives.
Fire Safety
Fire can be dangerous to human life, causing burns, acute injuries, smoke inhalation, and even death. In the most severe cases, we advise that fire incidents should be handled immediately by emergency responders. Homes, large structures, and established organizations are constantly at risk of fire. Once a fire starts in your area, you only have a few minutes to evacuate; otherwise, the consequences could be dire.
Getting out of a fire depends on two key factors: having functioning smoke alarms and accessible fire exits. However, it primarily relies on your emergency response and how prepared you are for such incidents. Although you may not be a professional firefighter, everyone should have some basic first aid knowledge related to fire safety. A small fire can often be extinguished using a fire extinguisher, and minor injuries can be treated, helping to prevent major losses.
Most Common Causes of Fire
- Cooking Accidents: Kitchen negligence can lead to fires, such as allowing saucepan handles to stick out over the edge of the stove or leaving children unattended in front of a hot stove. Additionally, keeping towels, loose clothing, paper, or plastic bags close to a flame can pose serious risks.
- Poor Electrical Distribution: Unused electrical appliances can cause fires in many areas. It’s important to disconnect extensions or adapters that are not in use. Overloading electrical circuits can also lead to fires.
- Misuse of Electrical Equipment: Fires can result from short circuits, improper use, or overuse of electrical equipment such as electric blankets, heaters, microwaves, or electric ovens.
- Improper Use of Smokers and Garden Grills: Household smokers and garden grills can lead to fires due to incorrect fuel dosage or improper combustion.
- Matches: Keeping matches within reach of children poses a fire risk. Bringing fire close to flammable objects like curtains, leather furniture, or gas cylinders can also be dangerous
- Lit Cigarette Butts: Lit cigarette butts can ignite fires in gardens and can quickly lead to dangerous outdoor fires.
- Candles: Many parts of Nigeria have experienced fires caused by lighted candles. In fact, a fire is reported every 48 seconds due to the use of lighted candles.
- Flammable Chemicals: Chemicals such as adhesives, oil paints, solvents, and detergents are highly flammable. If stored in rooms with high temperatures or exposed to minimal contact with fire, they can cause explosions.
- Batteries: Allowing lithium batteries in remote controls or laptops to come into contact with fire can lead to major explosions.
- Aerosol Cans: Products such as deodorants, perfumes, and hairsprays are highly flammable and can ignite quickly, causing fires.
RELATED SERVICES
TYPES OF FIRES
-
“A” Type Fires
These fires are caused by materials such as paper, cloth, and wood. Earlier, soda-acid extinguishers were used to combat this type of fire, but now CO2 and water extinguishers are commonly employed.
-
“B” Type Fires
These fires are fueled by substances such as diesel and petrol. Sand or thick cloth can be used to extinguish these fires. Previously, air-foam extinguishers were used, but now chemical foam extinguishers are preferred.
-
“C” Type Fires
These fires are caused by gas or electricity. CO2 extinguishers are typically used to put out these fires.
-
“D” Type Fires
These fires are caused by chemicals. When using extinguishers for this type of fire, covering the face with a wet cloth is essential.
Colour Code for Extinguishers
- A – RED
- B – CREAM
- C – BLACK
- D – BLUE
In some extinguishers the colour code will be indicated as stickers.
READ ALSO
About Extinguishers
- Inspection of extinguishers should be conducted annually.
- If the weight loss exceeds 10%, refilling is necessary.
- Dry powder cartridges should be recharged every two years.
- Halon gas extinguishers can be used on electronic items such as TVs and computers, but this gas is toxic. Exercise caution when using it.
- CO2 gas extinguishers are effective only indoors.
- Use only CO2 gas extinguishers on important documents, books, electronic items, etc.

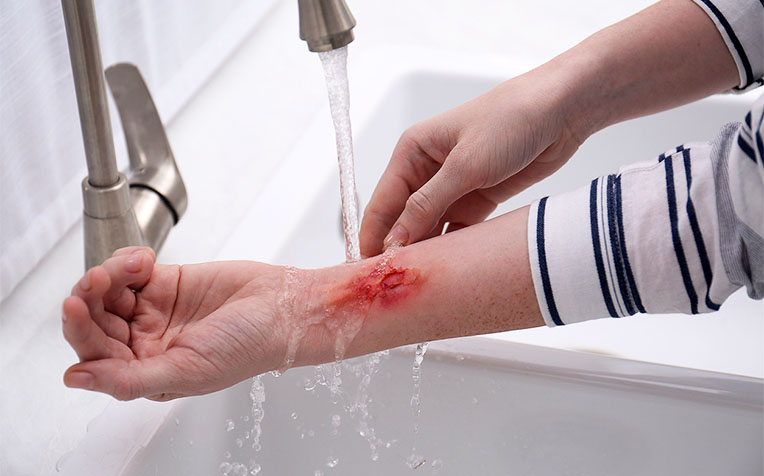
BURNS
A burn is an injury that results from heat, chemical agents, or radiation. It may vary in depth, size, and severity, causing injury to the cells in the affected area.
First Aid for General Burns
- Immerse the burned area in cold water.
- Apply freshly ironed or laundered clothes that have been wrung out in ice water.
- Do not break blisters or remove tissue.
- Avoid using antiseptic preparations, ointments, sprays, or home remedies on severe burns.
- Do not remove adhered particles of charred clothing.
- If the hands are involved, keep them elevated above the level of the victim’s heart.
- Keep burned feet or legs elevated; the victim should not be allowed to walk.
- Do not delay in seeking medical help if the burn is severe.
- If the burn is large, lay the casualty down as shown in the figure.
Thermal Burns
Thermal burns are caused by exposure to hot solids, liquids, and gases, or fire.
First Aid for Thermal Burns
- Monitor the airway, breathing, and circulation.
- Control bleeding.
- Remove all jewelry from the area, unless the casualty objects.
- Apply cool water to the affected area or submerge it in cool water. DO NOT USE ICE OR ICE WATER.
- Gently remove clothing from the burned area. DO NOT REMOVE CLOTHING THAT IS STICKING TO THE SKIN.
- Cover the area with a dry, sterile dressing, if possible.
- Treat for shock.
Ways You Can Prevent a Fire Today
- Put out candle lights before going to bed.
- When cooking in the kitchen, keep towels, pot holders, and soft curtains away from the flames.
- Store matches, lighters, and other ignitable substances in a secure location out of the reach of children, and only use lighters with child-resistant features.
- Check your chimney and heating equipment annually with a certified professional.
- Use a glass or metal fire screen large enough to catch sparks and rolling logs to keep fire in your fireplace.
- Have wood and coal stoves, fireplaces, chimneys, and furnaces professionally inspected and cleaned once a year.
- Keep candles at least 12 inches away from anything that can burn, such as bedding, curtains, or clothing.
- Clean surfaces regularly to avoid the buildup of grease.
- Check the kitchen every night before going to bed to ensure that all ovens and stoves are off, and make sure all appliances are turned off, especially those plugged into the wall.
- Place every potential source of fire, like paper, clothing, or rugs, at least three feet away from the stove, fireplace, or heater.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the first aid treatment for fire?
Place the area burned under running water for about 10 minutes. If the burn is on the face, apply a wet cloth to ease the pain.
-
What is the first aid for a fire building?
Avoid walking around and maintain calm to prevent the fire from escalating. Look for all possible ways to get the casualty to the ground, either using a fire blanket or heavy fabric such as a coat or blanket.
-
What is the best immediate treatment for burns?
Put the burn in cool tap water or apply a wet compress if it is on the face. Apply petroleum jelly two to three times daily. Avoid using ointments, toothpaste, or butter, as these can lead to infection.
-
How do you treat a burn in an emergency?
Continue flushing the area for up to 10 minutes, regardless of the degree of the burn. Do not apply ice, ointments, butter, or other “home remedies.” Remove all clothing or garments to reduce contact time with hot items.
-
What is a fire accident?
Fire accidents are incidents caused by fire that can lead to burn injuries, resulting in scars, pain, disability, or disfigurement in the casualty, and in some cases, it can lead to death.